|

The
Republic of India, commonly known as India,
is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest
country by geographical area, the second most populous
country, and the most populous liberal democracy in the
world. India has a coastline of over seven thousand kilometres, bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south,
the Arabian Sea on the west, and the Bay of Bengal on
the east. India borders Pakistan to the west; People's
Republic of China, Nepal and Bhutan to the north-east;
and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east.
My
father was born in Madras in the 1930s. My grandmother
was a ballerina touring the world and a colonial.
My father was raised in Bombay and Shimla, and educated
at a private school in Kodaikanal in the 1940s.
Hence, I have a soft spot for this part of the world. NK
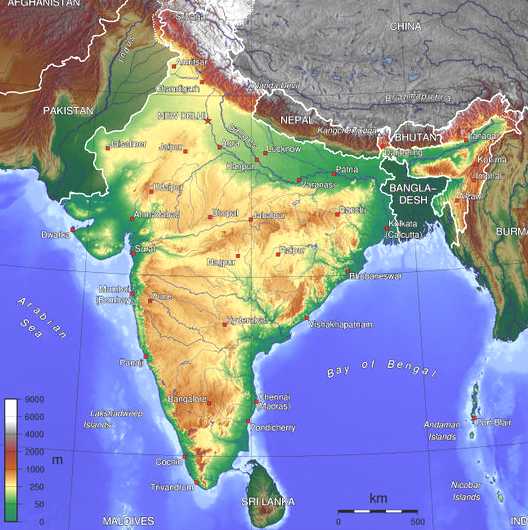
Map
of India, the land mass bounded by the Arabian Sea and
the Bay of Bengal
Home
to the Indus Valley Civilization and a region of
historic trade routes and vast empires, the Indian
subcontinent was identified with its commercial and
cultural wealth for much of its long history. Four major
world religions, Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikhism
originated here, while Islam, Christianity, Judaism and
Zoroastrianism, arrived in the first millennium CE and
shaped India's variegated culture. Despite countless
invasions over thousands of years, Indian culture and
society has been so resilient, that it has either thrown
away or completely absorbed any foreign influences, with
the social fabric largely remaining unchanged and
intact. The present modern democratic nation-state of
India emerged in 1947, after it overthrew foreign
occupation by widespread use of nonviolent resistance.
With
the world's fourth largest economy in purchasing power
and the second fastest growing large economy, India has
made rapid progress in the last decade, especially in
information technology. In addition, its successful
space programme, a modern technologically advanced
defence forces aided by a nuclear
deterrence has led to India's current status as an
emerging superpower in international relations. It is
also a member of the G4. Although India's standard of
living is projected to rise sharply in the next
half-century, it currently battles high levels of poverty,
persistent malnutrition, and environmental degradation.
A multi-lingual, multi-ethnic society, India is also
home to a diversity of wildlife in a variety of
protected habitats.
India,
world location map
POLITICS
For
most of its democratic history, India has been ruled by
the Indian National Congress at the federal level, state
politics have been dominated by national parties like
Indian National Congress, Bharatiya Janata Party,
Communists and some regional parties. Till 1990, Indian
National Congress party enjoyed a parliamentary majority
barring two brief periods during the 1970s and late
1980s. This rule was interrupted between 1977 to 1980,
when the Janata Party won the election owing to public
discontent with the "Emergency" declared by
the then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi. The Janata Dal
coalition, called the National Front, won elections in
1989, but its government managed to hold on to power for
only two years. Between 1996 and 1998, there was a
period of political flux with the government being
formed first by the Bharatiya Janata Party followed by
the United Front coalition. In 1998, the BJP formed the
National Democratic Alliance (NDA) with smaller regional
parties, and became the first non-Congress and coalition
government to complete a full five-year term. The 2004
Indian elections saw the Indian National Congress
winning the largest number of seats to form a government
leading the United Progressive Alliance, supported by
left-leaning and other parties opposed to the BJP.
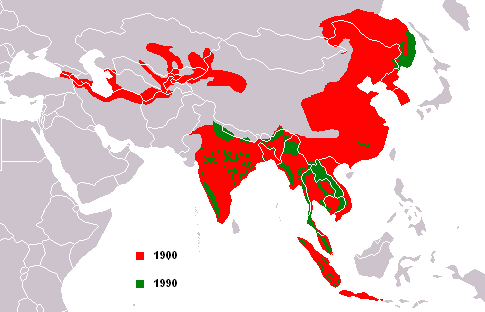
Tiger
population world location map
GEOGRAPHY
India
constitutes the major portion of the Indian
subcontinent, which sits atop the Indian Plate and the
northwesterly portion of the Indo-Australian Plate.
India's northern and northeastern states are partially
situated in the Himalayan Range. The rest of northern,
central, and eastern India consists of the fertile Indo-Gangetic
Plain. In the west, bordering southeastern Pakistan,
lies the Thar Desert. Southern India is almost entirely
composed of the peninsular Deccan plateau, which is
flanked by two hilly coastal ranges, the Western Ghats
and the Eastern Ghats.
India
is home to several major rivers, including the Ganges,
the Brahmaputra, the Yamuna, the Godavari, the Kaveri,
the Narmada, and the Krishna. India has three
archipelagos — Lakshadweep, which lies off the
southwestern coast; the volcanic Andaman and Nicobar
Islands island chain to the southeast, and the
Sunderbans in the Ganges Delta of West Bengal.
The
climate in India varies from tropical in the south to
more temperate in the Himalayan north, where elevated
regions receive sustained winter snowfall. India's
climate is strongly influenced by the Himalayas and the
Thar Desert. The Himalayas, along with the Hindu Kush
mountains in Pakistan, prevent cold Central Asian
katabatic winds from blowing in. This keeps the bulk of
the Indian subcontinent warmer than most locations at
similar latitudes. The Thar Desert is responsible for
attracting the moisture-laden summer monsoon winds that,
between June and September, provide most of India's rainfall.

Apatani
tribal women in Arunachal Pradesh
DEMOGRAPHICS
With
an estimated population of 1.1 billion, India is the
world's second most populous country. Almost 70% of
Indians reside in rural areas, although in recent
decades migration to larger cities has led to the
exponential rise in the urban population. India's
largest urban agglomerations are Mumbai, Pune, Kolkata,
Delhi, Chennai , Bangalore and Hyderabad.
India
is home to two major linguistic families: Indo-Aryan
(spoken by about 74% of the population) and Dravidian
(spoken by about 24%). Other languages spoken in India
come from the Austro-Asiatic and Tibeto-Burman
linguistic families. The Indian constitution recognises
23 official languages. Hindi and English are used by the
Union Government of India for official purposes, wherein
Hindi has a de jure priority. Sanskrit and Tamil
enjoy classical language status in India. The number of
dialects in India is as high as 1,652.
Although
80.5% of Indians report themselves as Hindus, India's
Muslim population is the world's second largest; they
constitute 13.4% of the population. Other religious
groups include Christians (2.3%), Sikhs (1.9%),
Buddhists (0.8%), Jains (0.4%), Jews, Ayyavazhi's,
Zoroastrians, Bahá'ís and others.
At
the time of India's emergence as a nation-state in 1947,
India's literacy rate was 11%. Since then, it has
increased to 68.6% (58.25% for females and 78.8% of
males). The state of Kerala has the highest literacy
rate (91%); Bihar has the lowest (47%). The national sex
ratio is 944 females per 1,000 males. India's median age
is 24.66, and the population growth rate of 1.38% per
annum; there are 22.32 births per 1,000 people.

PRIME
MINISTER - Narendra G Modi is making it one of his goals tackle the
Himalayan problem that faces his country, in squaring up to the pollution
of India's Holy River.
SHIPBUILDING
APRIL 2013 - Indian ship building set to recover lost glory?
Resilient ship building brings hope of its revival and escalated growth.
India’s tryst with
American history can be traced back to the role Indian ship building played in the creation of the U.S. National Anthem “The Star-Spangled Banner”. The lyrics came from “Defence of Fort McHenry”, a poem written in 1814 by Francis Scott Key when aboard the Minden, a vessel that was built in India. This vessel, Minden, was built of teak by Jamshedji Bomanji Wadia and launched in 1810 from the Duncan Docks in Bombay (now Mumbai), India.
Because of this exquisite ship building facility at that time, Bombay became a strategic port for the British colonial undertakings in Asia and Minden providing the first and only
British ship of the line built out of the limits of the Mother Country until then. The
Royal Navy came to admire the skill of its architects, for the superiority of its timber, and for the excellence of its docks, giving Bombay a distinguished place among naval arsenals”.
From time immemorial ship building activity in India has been known for its splendid quality. Through the ages this industry continued to enjoy its heydays even until a century back. In fact, from ancient times India’s prowess as a ship builder went unchallenged.
The name Lothal stands out as the oldest Indian known dock in the world that existed during the Bronze Age (from 3300 to 1200 BC). The Iron Age (1500 to 500 BC) saw Rig Veda ships commanding a lot of respect among the contemporary seafaring nations. In 326 BC, during the Nanda Period, Alexander the Great acquired his large
boats that were built in Punjab by a tribe. The dominance of ship building activity continued through the ages that in 20 B.C. during the Pandya Dynasty Indian ship builders came to be known for their rich knowledge and expertise of
metallurgy. The bolts used in ship building were of Muntz alloy (60% Copper and 40% Zinc) and the workmen were skillful in working with other copper alloys such as brass and bronze.
Throughout recorded history the world-wide recognition for India’s ship building panache was acknowledged and responsible for various
naval powers to source their requirement of ships from the different shipyards of India. The invading forces of the past two millennium which establish their empires in the country also did not so much as venture out to establish a
maritime power which could have benefitted Indian shipping Yet ship building did make a big hit as is well known.
Amongst the various manufacturing industries, the Indian government considers shipbuilding industry to have the highest investment and employment multiplier effect says Cdr. S Navaneetha Krishnan of the Indian Navy. In his well referred book “Prosperous Nation Building through Shipbuilding”, published recently he brings out the resilience and potentiality of the present state of the industry.”
Representing a mere 1.3% of the global ship building share, India’s present strength include about 10 government owned ship yards and around 50 in the private sector. According to the World Economic Forum’s Global competitiveness Index (GCI) few years ago, India continued to score well in indicator related to innovation and sophistication of firm operation as well as in the adoption of technologies from abroad. However, as a result of the down turn the efforts to reduce the high budget deficit remained a big challenge.
Considering ship building to be the biggest force multiplier for the economy, the Prime Minister Dr Manmohan Singh has indentified ship building sector to be the vehicle for creating employment and wealth for the country. He said, “Amongst the manufacturing industries the ship building industry has been identified to have the highest investment and employment multiplier effect.”
In the recent national budget the government of India after several years made a beginning - giving a minor sop to the ship building industry by exempting ship builders from payment of excise duty which is of around 5 per cent.
Cdr Krishnan states in his book that the Maritime Agenda 2010-2020, the government proposes giving a boost to Indian ship building in order to achieve a global market share of 5 per cent by 2020. It also aspires to develop a strong ancillary base in the country. Additional it plans to generate 2.5 million jobs in ship building industry alone and to develop a strong Research and Development facilities and design capabilities for commercial ship building.
A rewarding exercise to resolve various problems could be to involve ship building professionals in the ship building policy making. Throw open sourcing of the Indian defense requirements to the Indian manufacturers instead the current practice of sourcing most of the naval needs from amongst foreign manufacturers. Private sector companies should be involved in
warship building.

TECHNOLOGY
STRATEGY BOARD - 12
MARCH 2013
The Technology Strategy Board (TSB) and the Indian Government’s Department of Science and Technology have agreed to undertake a joint programme to support innovative UK and Indian businesses which are working together on the commercialisation of research in a range of key areas including
energy and healthcare. The ‘Programme of Co-operation ’was signed at an international reception held at the Innovate UK conference in London.
The agreement is the first international partnership the Technology Strategy Board has signed outside of Europe. The Programme of Co-operation will see the TSB and the Indian Global Innovation and Technology Alliance (GITA), sponsored by the Indian Government, supporting
UK and Indian businesses and academics in joint R&D and innovation projects over a three year period. The Technology Strategy Board will commit up to £5m to the
programme.
On signing the agreement Iain Gray, Chief Executive of the
Technology Strategy
Board, said; “These programmes not only help build and strengthen links between countries but will help build the international partnerships between businesses so vital in today’s global economy”.
This programme is the first agreed between the two organisations and is expected to expand further over time, for the mutual benefit of businesses from both countries.
India is a rapidly growing economy which provides huge opportunities for innovative UK businesses. By working with similar Indian businesses, UK companies are able to understand the needs of this vibrant and fast-moving market. The support of the Technology Strategy Board will help them build partnerships and will support joint,
collaborative R&D and
innovation projects.
Innovate
UK Technology Strategy Board
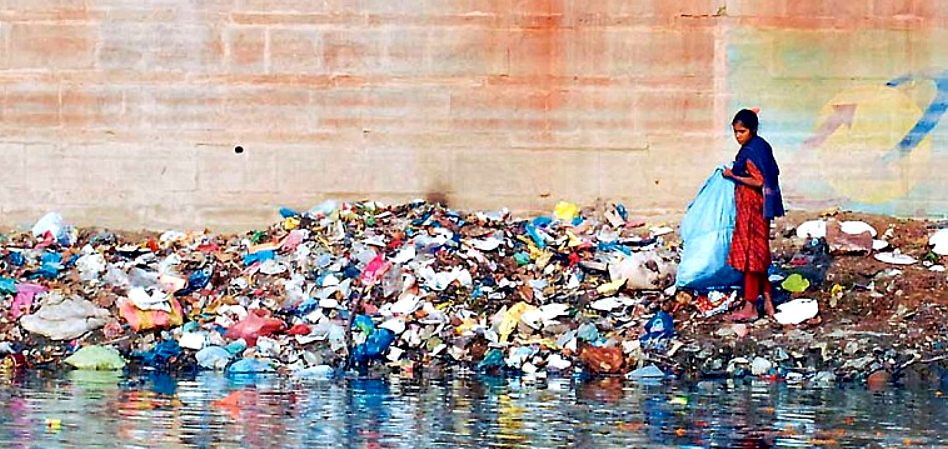

HOLY
MOTHER GANGA - The River Ganges, for long described as the giver of
life, is so polluted that it contains dangerous levels of industrial
waste. It would take some serious effort to even begin to get this river
back to its natural state, before the intervention of man. In all nature
their is a natural balance that as intelligent invaders, we should strive
to conserve. River pollution is though not unusual. Many European rivers
have been so polluted in the past that just a quick swim in the water
meant death. The River
Thames was once such waterway in years gone by.
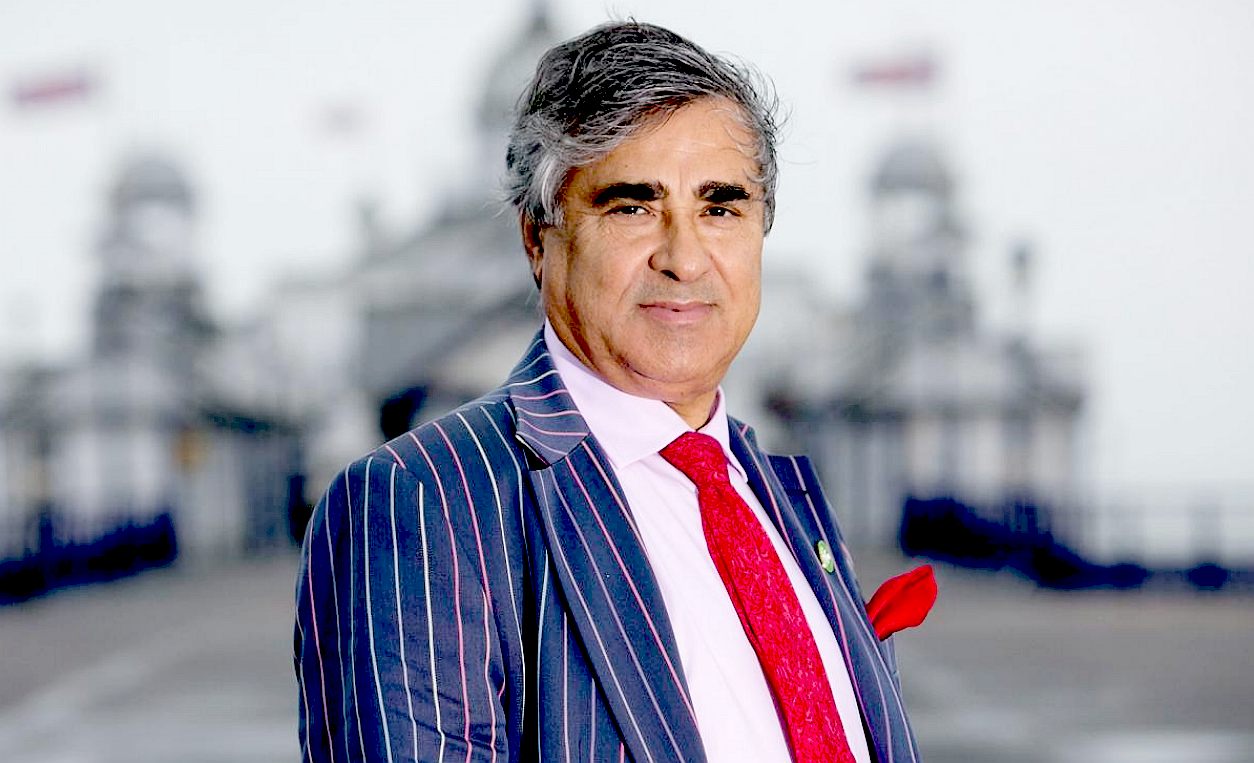

ABID
GULZAR - Born in India, Mr Gulzar,
once a leather technologist, operates hotels in Eastbourne
in England, with his latest acquisition being a grade II* listed pier
that is much in need or repair. Could it be that Narendra Modi and Abid
Gulzar manage to conserve heritage on opposite sides of the planet, beginning
in 2016. Eastbourne Pier suffered a fire that destroyed an iconic part of
the Victorian
structure, but the previous owners accepted an insurance payout and then
sold the historic seaside attraction for an undisclosed sum - without
restoring the music pavilion. Abid Gulzar is now faced with mounting rebuild
costs with a limited income from his hotels, though he could sell another
hotel to live up to his stated intention to: "Make this pier the best
in Britain." Possibly, a statement too farm since Clevedon
Pier is a grade I listed building and architecturally far superior.
TATA
Tata Group is an Indian multinational conglomerate company headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. It encompasses seven business sectors: communications and information technology, engineering, materials, services, energy, consumer products and chemicals. Tata Group was founded in 1868 by Jamsetji Tata as a trading company. It has operations in more than 80 countries across six continents. Tata Group has over 100 operating companies each of them operates independently out of them 32 are publicly
listed. The major Tata companies are Tata Steel, Tata Motors, Tata Consultancy Services (TCS), Tata Power, Tata Chemicals, Tata Global Beverages, Tata Teleservices, Titan Industries, Tata Communications and Taj Hotels. The combined market capitalisation of all the 32 listed Tata companies was $89.88 billion as of March 2012. Tata receives more than 58% of its revenue from outside India.
Tata Group remains a family-owned business, as the descendants of the founder (from the Tata family) owns majority stake in the company. The current chairman of the Tata group is Cyrus Pallonji Mistry, who took over from
Ratan Tata in 2012. Tata Sons is the promoter of all key Tata companies and holds the bulk of shareholding in these companies. The chairman of Tata Sons has traditionally been the chairman of the Tata group. About 66% of the equity capital of Tata Sons is held by philanthropic trusts endowed by members of the Tata family.
The Tata Group and its companies & enterprises is perceived to be India's best-known global brand within and outside the country as per an ASSOCHAM survey. The 2009, annual survey by the Reputation Institute ranked Tata Group as the 11th most reputable company in the world. The survey included 600 global companies. The Tata Group has helped establish and finance numerous quality research, educational and cultural institutes in India.
The group was awarded the Carnegie Medal of Philanthropy in 2007 in recognition of its long history of philanthropic activities.
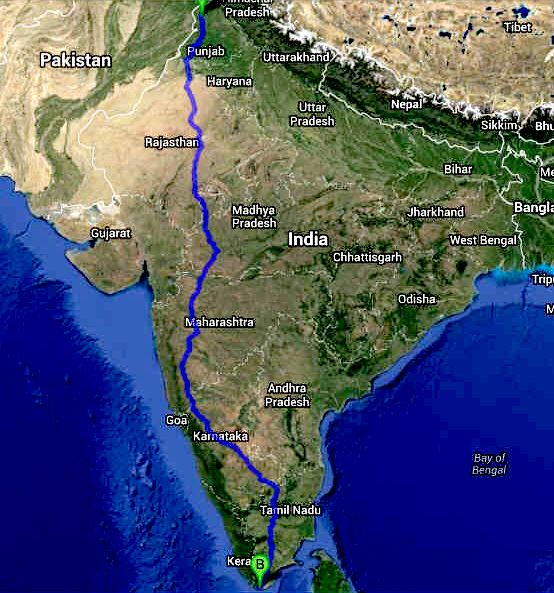
The
Cannonball International EV series of road runs is open to all comers
provided they hold a valid driving licence and stay within the speed
limits. This is an event for people who care about conserving our planet.
Cars must be based on production running gear, though modification of
drive and battery
or fuel cell
storage is allowed.
Make politicians around the world take notice of by attempting to equal
the speeds and endurance of petrol
and diesel powered
vehicles.
AMRITSAR
to NAGERCOIL - TRANS-INDIA
CANNONBALL EV RUN SUGGESTED STOPS
|
START
|
AMRITSAR
|
NORTH
|
KILOMETERS
|
|
1st
STOP
|
Sri
Muktsar Sahib
|
Punjab
|
167
|
|
2nd
STOP
|
Hanumangarh
|
Rajasthan
|
284
|
|
3rd
STOP
|
Mahajan
|
Rajasthan
|
401
|
|
4th
STOP
|
Bikanar
|
Rajasthan
|
516
|
|
5th
STOP
|
Ajmer
|
Rajasthan
|
714
|
|
6th
STOP
|
Bhilwara
|
Rajasthan
|
843
|
|
7th
STOP
|
Pratapgarh
|
Rajasthan
|
1016
|
|
8th
STOP
|
Ratlam
|
Madhya
Pradesh
|
1106
|
|
9th
STOP
|
Palasner
|
Maharashtra
|
1358
|
|
10th
STOP
|
Chalisgaon
|
Maharashtra
|
1497
|
|
11th
STOP
|
Aurangabad
|
Maharashtra
|
1590
|
|
12th
STOP
|
Beed
|
Maharashtra
|
1717
|
|
13th
STOP
|
Solapur
|
Maharashtra
|
1896
|
|
14th
STOP
|
Bijapur,
|
Karnataka
|
1995
|
|
15th
STOP
|
Gadag
|
Karnataka
|
2179
|
|
16th
STOP
|
Davangere
|
Karnataka
|
2335
|
|
17th
STOP
|
Chiknayakanhalli
|
Karnataka
|
2508
|
|
18th
STOP
|
Mysore
|
Karnataka
|
2657
|
|
19th
STOP
|
Chamaranjanagra
|
Karnataka
|
2758
|
|
20th
STOP
|
Sathyamangalam
|
Tamil
Nadu
|
2815
|
|
21st
STOP
|
Tiruppur
|
Tamil
Nadu
|
2925
|
|
22nd
STOP
|
Dindigul
|
Tamil
Nadu
|
2975
|
|
23rd
STOP
|
Madurai
|
Tamil
Nadu
|
3037
|
|
24th
STOP
|
Kovilpatti
|
Tamil
Nadu
|
3125
|
|
25th
STOP
|
Tirunelveli
|
Tamil
Nadu
|
3181
|
|
FINISH
|
NAGERCOIL
|
SOUTH
|
3,264
|
TATA
MOTORS
Tata Motors Limited (formerly TELCO) is an Indian multinational automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India and a subsidiary of the Tata Group. Its products include passenger cars, trucks, vans, coaches, buses and military vehicles. It is the world's eighteenth-largest motor vehicle manufacturing company, fourth-largest truck manufacturer and second-largest bus manufacturer by volume.
Tata Motors has auto manufacturing and assembly plants in Jamshedpur, Pantnagar, Lucknow, Sanand, Dharwad and Pune, India, and in Argentina, South Africa, Thailand and the United Kingdom. It has research and development centres in Pune, Jamshedpur, Lucknow and Dharwad, India, and in South Korea, Spain, and the United Kingdom. It has a bus manufacturing joint venture with Marcopolo S.A., Tata Marcopolo, and a construction equipment manufacturing joint venture with Hitachi, Telcon Construction Solutions.
Founded in 1945 as a manufacturer of locomotives, the company manufactured its first commercial vehicle in 1954 in a collaboration with Daimler-Benz AG, which ended in 1969. Tata Motors entered the passenger vehicle market in 1991 with the launch of the Tata Sierra and in 1998 launched the first fully indigenous Indian passenger car, the Indica. Tata Motors acquired the South Korean truck manufacturer Daewoo Commercial Vehicles Company in 2004 and the British premium car maker Jaguar Land Rover in 2008.
Tata Motors is listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange, where it is a constituent of the BSE SENSEX index, the National Stock Exchange of India and the
New York Stock
Exchange. Tata Motors is ranked 314th in the 2012 Fortune Global 500 ranking of the world's biggest corporations.
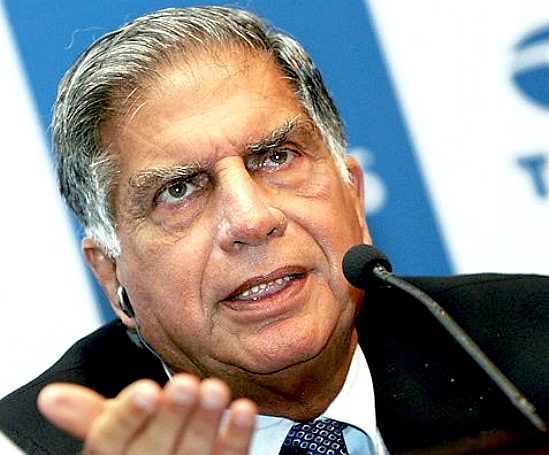

SIR
RATAN TATA - Apart from his businesses, Sir Ratan was a Global
Ocean Commissioner during the compiling of a report on the state of the
world's oceans in 2014 and 2015.
TATA HISTORY
Tata entered the commercial vehicle sector in 1954 after forming a joint venture with Daimler-Benz of Germany. After years of dominating the commercial vehicle market in India, Tata Motors entered the passenger vehicle market in 1991 by launching the Tata Sierra, a multi utility vehicle. After the launch of three more vehicles, Tata Estate (1992; a station wagon design based on the earlier 'TataMobile' (1989), a light commercial vehicle), Tata Sumo (1994; LCV) and Tata Safari (1998; India's first sports utility vehicle).
Tata launched the Indica in 1998, the first fully indigenous Indian passenger car. Although initially criticised by auto-analysts, its excellent fuel economy, powerful engine and an aggressive marketing strategy made it one of the best selling cars in the history of the Indian automobile industry. A newer version of the car, named Indica V2, was a major improvement over the previous version and quickly became a mass-favorite. Tata Motors also successfully exported large quantities of the car to South Africa. The success of Indica played a key role in the growth of Tata Motors.
In 2004 Tata Motors acquired Daewoo's South Korea-based truck manufacturing unit, Daewoo Commercial Vehicles Company, later renamed Tata Daewoo.
In 2005, Tata Motors acquired a 21% controlling stake in the Spanish bus and coach manufacturer Hispano Carrocera. Tata Motors continued its market area expansion through the introduction of new products such as buses (Starbus & Globus, jointly developed with subsidiary Hispano Carrocera) and trucks (Novus, jointly developed with subsidiary Tata Daewoo).
In 2006, Tata formed a joint venture with the Brazil-based Marcopolo, Tata Marcopolo Bus, to manufacture fully built buses and coaches.
In 2008, Tata Motors acquired the British car maker Jaguar Land Rover, manufacturer of the Jaguar, Land Rover and Daimler luxury car brands, from Ford Motor Company.
In May 2009 Tata unveiled the Tata World Truck range jointly developed with Tata Daewoo. Debuting in South Korea, South Africa, the SAARC countries and the Middle-East by the end of 2009.
Tata acquired full ownership of Hispano Carrocera in 2009.
In 2010, Tata Motors acquired an 80% stake in the Italy-based design and engineering company Trilix for a consideration of €1.85 million. The acquisition formed part of the company's plan to enhance its styling and design capabilities.
In 2012, Tata Motors announced it will invest around 6 billion on developing Futuristic Infantry Combat Vehicles in collaboration with
DRDO.
DEFENCE
RESEARCH DEVELOPMENT ORGANISATION (DRDO)
The
DRDO is an agency of the Republic of India, responsible for the development of technology for use by the military, headquartered in New Delhi, India. It was formed in 1958 by the merger of the Technical Development Establishment and the Directorate of Technical Development and Production with the Defence Science Organisation.
DRDO has a network of 52 laboratories which are deeply engaged in developing defence technologies covering various fields, like aeronautics, armaments, electronic and computer sciences, human resource development, life sciences, materials, missiles, combat vehicles development and naval research and development. The organization includes more than 5,000 scientists and about 25,000 other scientific, technical and supporting personnel.

NAVAL RESEARCH and DEVELOPMENT
Sonars
DRDO, BEL and the Indian Navy have developed and productionized a range of sonars and related systems for the Indian Navy's frontline combat ships.
These include:
APSOH (Advanced Panoramic SOnar Hull mounted),
HUMVAD (Hull Mounted Variable Depth sonar),
HUMSA (Follow on to the APSOH series; the acronym HUMSA stands for Hull Mounted Sonar Array),
Nagan (Towed Array Sonar),
Panchendriya (Submarine sonar and fire control system).
Other sonars such as the airborne sonar Mihir are in trials, whilst work is proceeding apace on a new generation of sonars.
Sonars may be considered one of DRDO's most successful achievements as the Indian Navy's most powerful ships rely on DRDO made sonars. The standard fit for a front line naval ship would include the HUMSA-NG hull mounted sonar and the Nagan towed array sonar. The Mihir is a dunking sonar meant for use by the Naval ALH, working in conjunction with its Tadpole sonobuoy. The Panchendriya is in production for the Kilo class
submarine
upgrades.
Torpedoes
DRDO is currently engaged in developing multiple torpedo designs. These include a lightweight torpedo that has been accepted by the Navy and cleared for production.
Under development
Advanced Light Torpedo Shyena is an advanced experimental torpedo developed by the Naval Scientific and Technological Laboratory (NSTL), a DRDO wing. Development was started in 1990.
NSTL Advanced Lightweight Torpedo
NSTL Varunastra Heavy Weight Torpedo: The heavy weight wire-guided torpedo called Varunastra and Thakshak thermal torpedo are suitable for use against both ships and
submarines. The electrically powered Varunastra is stated to be in production.
The DRDO also developed and productionised a microprocessor controlled triple tube torpedo launcher for the Indian Navy as well as a towed torpedo decoy.
Other projects
These have included indigenisation of various components (for instance, adsorbent material for submarines, radar components, naval ship signature reduction efforts and materials technology). DRDO has played a significant role in the development of warship grade steel in India and its productionisation. DRDO has also assisted private industry in developing EW trainers, ship simulators for training and health monitoring systems for onboard equipment. Other equipment for the Navy includes underwater telephone sets, and VLF communication equipment, for the Navy's submarines. DRDO's IRDE has also developed optronic fire control systems for the Navy's and the
Coast Guard's ships.
Information command and control systems
DRDO's labs have been part of projects to develop sophisticated command and control systems for the Navy, such as the EMCCA (Equipment Modular for Command and Control Application) which ties together various sensors and data systems. The EMCCA system gives commanders on the ship a consolidated tactical picture and adds to the ship’s maritime combat power.
DRDO labs are also engaged in supporting the Navy's ambitious naval enterprise wide networking system, a program to link all naval assets together via datalinks, for sharing tactical information.
Mines and targets
Three kinds of mines, processor based mine, moored mine and processor based exercise mine are in production for the Navy. Targets developed for the Navy include a static target called the Versatile Acoustic target and a mobile target called the programmable deep mobile target (PDMT).
In development
A Submarine Escape set, used by crew to escape from abandoned submarines. The set consists of breathing apparatus and Hydro-suit.
New generation Sonars and EW equipment.
Heavyweight torpedoes, underwater remotely operated vehicles, improved signature reduction technology for naval applications.

OTHER PROJECTS
Command and control software and decision-making tools
Tactical tools for wargaming: Shatranj and Sangram for the Army, Sagar for the Navy and air war software for the Air Force. All these systems are operational with the respective services.
C3I systems: DRDO, in cooperation with BEL and private industry has developed several critical C3I (command, control, communications and intelligence systems) for the armed services. Under the project "Shakti", the Indian Army aims to spend
US$300 million to network all its artillery guns using the ACCS (Artillery Command and Control System). Developed by DRDO's Centre for Artificial Intelligence & Robotics, the system comprises computers and intelligent terminals connected as a wide area network. Its main subsystems are the artillery computer center,
battery computer, remote access terminal and a gun display unit. The ACCS is expected to improve the Army's artillery operations by a factor of 10 and allowing for more rapid and accurate firepower. The ACCS will also improve the ability of commanders to concentrate that firepower where it is most needed. The DRDO and BEL have also developed a Battle Management system for the Indian Army for its tanks and tactical units.
Other programs in development for the Army include Corps level information and decision making software and tools, intended to link all units together for effective C3I. These systems are in production at DRDO's production partner, Bharat Electronics Limited. These projects are being driven by the Indian Army Corps of Signals. The Indian Army is also moving towards extensive use of battlefield
computers. DRDO has also delivered projects such as the Combat Net Radio for enhancing the Army's communication hardware.
Data management and command and control systems for the Navy have been provided by the DRDO. The Navy is currently engaged in a naval networking project to network all its ships and shore establishments plus maritime patrol aircraft and sensors.
Radar netting and multi-sensor fusion software for linking the Indian Air Force's network of radars and airbases which have been successfully operationalised. Other systems include sophisticated and highly complex mission planning and C3I systems for missiles, such as the Agni and Prithvi ballistic missiles and the Brahmos cruise missile. These systems are common to all three services as all of them utilize different variants of these missiles.
Simulators and training tools: DRDO and private industry have collaborated on manufacturing a range of simulators and training devices for the three services, from entry level tests for prospective entrants to the Indian Air Force, to sophisticated simulators for fighter
aircraft, transports and
helicopters, tanks and gunnery devices.
Computing technologies
DRDO has worked extensively on high speed computing given its ramifications for most of its defence projects. These include
supercomputers for computational flow dynamics, to dedicated microprocessor designs manufactured in India for flight controllers and the like, to high speed computing boards built around Commercial Off The Shelf (COTS) components, similar to the latest trends in the defence industry.
Supercomputing: DRDO's ANURAG developed the PACE+ Supercomputer for strategic purposes for supporting its various programs. The initial version, as detailed in 1995, had the following specifications: The system delivered a sustained performance of more than 960 Mflops (million floating operations per second) for computational fluid dynamics programs. Pace-Plus included 32 advanced computing nodes, each with 64 megabytes(MB) of memory that can be expanded up to 256MB and a powerful front-end processor which is a hyperSPARC with a speed of 66/90/100 megahertz (MHz). Besides fluid dynamics, these high-speed computer systems were used in areas such as vision, medical imaging, signal processing, molecular modeling, neural networks and finite element analysis. The latest variant of the PACE series is the PACE ++, a 128 node parallel processing system. With a front-end processor, it has a distributed memory and message passing system. Under Project Chitra, the DRDO is implementing a system with a computational speed of 2-3 Teraflops utilizing commercial off the shelf components and the Open Source Linux Operating System.
Processors and other critical items: DRDO has developed a range of processors and application specific integrated circuits for its critical projects. Many of these systems are modular, in the sense that they can be reused across different projects. These include "Pythagoras processor" to convert cartesian to polar coordinates, ANUCO, a floating point coprocessor and several others, including the ANUPAMA 32-bit processor, which is being used in several DRDO projects.
Electronic components: one of the endeavours undertaken by the DRDO has been to create a substantial local design and development capability within India, both in the private and public sectors. This policy has led to several hard to obtain or otherwise denied items, being designed and manufactured in India. These include components such as radar subsystems (product specific travelling wave tubes) to components necessary for electronic warfare and other cutting edge projects. Today, there are a range of firms across India, which design and manufacture key components for DRDO, allowing it to source locally for quite a substantial chunk of its procurement. The DRDO has also endeavoured to use COTS (Commercial off the shelf) processors and technology, and follow Open Architecture standards, wherever possible, in order to pre-empt obsolescence issues and follow industry practise. One significant example is the development of an Open Architecture computer for the Light Combat Aircraft, based on the PowerPC architecture and VME64 standard. The earlier Mission computer utilizing Intel 486 DX chips has already seen success, with variants being present on the Su-30 MKI, Jaguar and MiG-27 Upgrades for the Indian Air Force.

OFFSHORE
WIND ENERGY 15 August 2013
LONDON
- India’s Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has published a report detailing the significant potential for offshore wind energy in the country.
Offshore Wind Potential Tamil Nadu, India was officially released this week at Delhi’s National Consultation on Development of Offshore
Wind Energy in India.
Already holding 40 percent of India’s onshore wind capacity, the state of Tamil Nadu had roughly 7 GW of installed wind power capacity as of mid-2012, according to government figures. Evaluating existing wind data in the area, the analysis looked at the region over a 10-year period. The report also proposed a wind measurement campaign and outlined a roadmap towards offshore wind power development.
Scottish consultancy Oldbaum Services delivered the report for the Centre for Wind Energy Technology (CWET) in Chennai as part of CWET/MNRE’s ongoing renewable energy knowledge exchange with the Scottish government. In a statement, Oldbaum Services stressed that a number of requirements need to be met prior to successful offshore wind development in India.
Poushali Maji, technical lead on the report, said, “This document outlines a development strategy for the offshore wind energy sector in India which currently does not exist in this country. With a 7500-km coastline and increasing energy demand, India has huge potential and they need to work towards the development of this sector.”
Oldbaum Services technical director Andy Oldroyd said, “Offshore wind in India is a new area with a growing need for energy and is a complex and complicated business. That’s why it’s important to understand the infrastructure and supply chain in place in India, and lessons learned in Europe, so that they can deliver offshore wind at as low a cost of
energy level as possible.”
According to the government’s draft offshore wind energy policy, released in May, obstacles to offshore wind deployment in India include resource identification, grid interconnection and operation, and the development of adequate transmission infrastructure.
Also at the National Consultation, MNRE secretary Ratan P Watal announced that a National Offshore Wind Energy Authority will be formed shortly by the ministry. The authority is planned as the central agency for offshore wind projects in the country, carrying out resource assessments and surveys and entering into contracts with project developers for offshore wind energy projects in India’s 12 nautical miles of territorial waters.
And B.K. Chaturvedi, a member of the Planning Commission, said that because the cost of power generated from offshore wind energy is greater than that generated from onshore, a future policy framework should address this differential. He said the Planning Commission “will ensure highest priority to the renewable energy sector in the country so that it moves forward to achieve energy security.”
A 2012 study by Scottish Development International showed India’s potential to establish two 1 GW wind farms off the coastlines of Rameshwaram and Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu.
India ranks fifth in the world in terms of installed wind energy capacity, with 18.5 GW as of January 2013.
In a third announcement this week, MNRE outlined a new “green energy corridor” project to facilitate the integration of renewable power into the nation’s grid. Germany will provide developmental and technical assistance and €1 billion in soft credit to finance the project, MNRE said.

MISS
INDIA
The 52nd edition of the Femina Miss India beauty pageant was held in Yash Raj Films Studios, Mumbai on March 28, 2015. Femina Miss India World 2015, Aditi Arya will represent India at Miss World 2015, Aafreen Vaz was crowned Femina Miss India Supranational 2015 and will represent India at Miss Supranational 2015, Vartika Singh was crowned Femina Miss India Grand 2015 and will represent India at Miss Grand International 2015 and Sushrii Shreya Mishraa of Odisha will represent India at Miss United Continent 2015'. The pageant was telecasted on Colors TV and Zoom (TV channel).
Aditi Arya is an Indian model and beauty pageant titleholder who was crowned Femina Miss India World in 2015. She will represent India at Miss World 2015, the international beauty pageant.
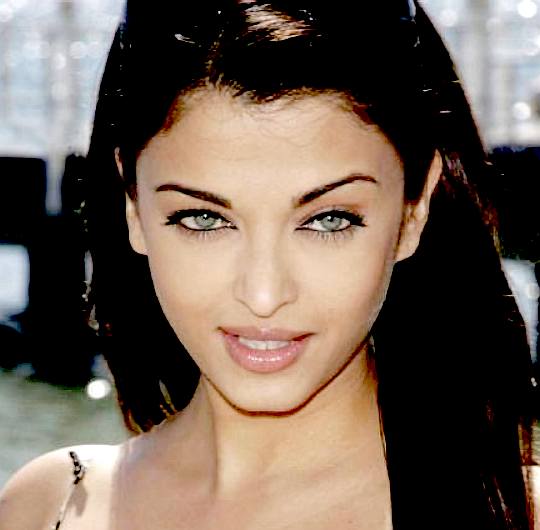


MISS WORLD 1994 - Aishwarya Rai
(right) was born on the 1st of November 1973). She is now known as Aishwarya Rai Bachchan
after her marriage.
She is an Indian actress and the winner of the Miss World pageant of 1994. Through her successful Bollywood career, she has established herself as one the most popular and high-profile celebrities in India. Rai has received several awards, including two Filmfare Awards from ten nominations. She was awarded the Padma Shri by the Government of India in 2009 and the Ordre des Arts et des Lettres by the Government of France in 2012. She is cited in the media as the
"most beautiful woman in the world".
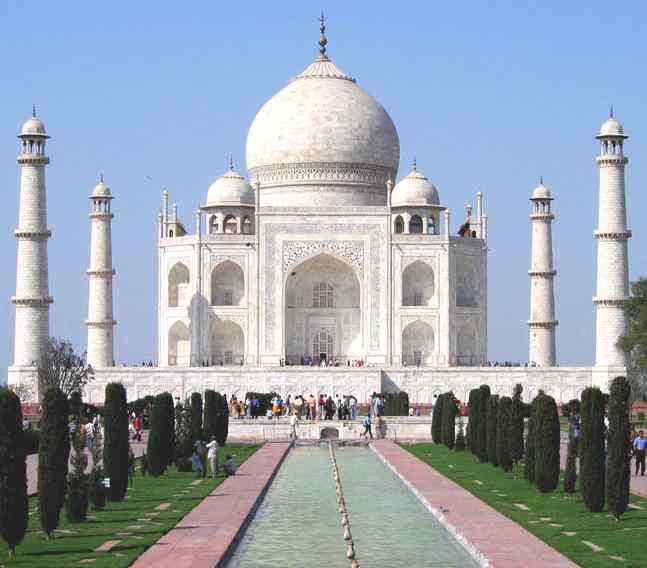

The
Taj Mahal in Agra
LINKS
and REFERENCE:
Indian
Express entertainment bollywood Aishwarya Rai and Kajol have the most
beautiful eyes deepika padukone http://indianexpress.com/article/entertainment/bollywood/aishwarya-rai-and-kajol-have-the-most-beautiful-eyes-deepika-padukone/
A ceasefire sponsored by the United
Nations in 1948 froze the positions of Indian
and Pakistani held
territory. As a consequence, the
region bordering Afghanistan is in
Pakistani-administered territory.
The
Weekly Standard The
New Great Game by Daniel Twining
Matthew,
K.M. (2006). Manorama Yearbook 2003. Malayala
Manorama, pg 524. ISBN 81-89004-07-7.
India
and the United Nations.
Indira
Gandhi Conservation Monitoring Centre (IGCMC), New
Delhi and the United
Nations Environmental Program (UNEP), World
Conservation Monitoring Center, Cambridge, UK.
2001. Biodiversity
profile for India.
Botanical
Survey of India. 1983. Flora and Vegetation of
India — An Outline. Botanical Survey of India,
Howrah. 24 pp.
Valmik
Thapar, Land of the Tiger: A Natural History of
the Indian Subcontinent, 1997.
Tritsch,
M.E. 2001. Wildlife of India Harper Collins,
London. 192 pages. ISBN 0-00-711062-6
K.
Praveen Karanth. (2006). Out-of-India
Gondwanan origin of some tropical Asian biota
Groombridge,
B. (ed). 1993. The 1994 IUCN Red List of
Threatened Animals. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland and
Cambridge, UK. lvi + 286 pp.
India's
Economic Growth Unexpectedly Quickens to 9.2%
"India
12th wealthiest nation in 2005: World Bank".
The
Hindustan Times.
"In
Pictures – Middle Class, or Upper Class? ".
India Together. Civil Society Information
Exchange.
"Revenue
surge boosts fiscal health". Business
Standard.
Census
of India 2001, Data on Religion. Census of
India.
Languages
of India. India image.
"Tamil
to be declared classical language". The
Hindu. 17 Sept. 2004
Matthew,
K.M. (2006). Manorama Yearbook 2003. Malayala
Manorama, pg 524.
The
Colonial Legacy: Myths and Popular Beliefs. Image-India.
Census
of India 2001, Data on Literacy. Census of
India.
Official
entry portal of the Government of India
Official
directory of Indian Government websites
CIA
World Factbook entry on India
Encyclopædia
Britannica entry on India
BBC
country profile of India
Satellite
images of India from Google Maps
India
at the Open Directory Project
Travel
to India: holidays,
flights, hotels
www.maritimeprofessional.com/Indian
ship building set to recover lost glory April 2013
www.renewableenergyworld.com/analysis
shows offshore wind power potential August 16 2013

DOOMSDAY
OPERATION GRAND SLAM -
Disillusioned extremists in Iran,
North Korea and Russia,
have grown impatient waiting for their leaders to act decisively, having
watched the Ukraine debacle
of Vladimir Putin rebound to weaken their CRINK
axis members. This despite Hamas launching against Israel and
Houthi attacks on the Red
Sea. All that had the effect of waking the sleeping giant: NATO.
They
hatch a plot to kidnap top politicians from the west to create confusion, as a
prelude to an all out cyber
nuclear first and second strike, having first stockpiled sufficient gold
and weapons reserves, and fallout bunkers for their cells, to be able to stage
a second wave of conventional attacks, to in effect, take over the world after
the nuclear holocaust they
have engineered. Including assassinating their jaded leaders: Xi
Jinping; Vladimir
Putin, Iranian Grand Ayatollah, Ali
Khamenei, and Kim
Jong Un, supreme leader of communist North
Korea.
|
India
in 2 minutes
- Youtube
|
India
& Youtube
|
|
India
travel Karala - Youtube
|
Snake
Chamer
- Youtube
|
|
Adelaide
Aden
- Yemen
Afghanistan
Africa
Alaska
Albania
Algeria
Amazon
Rainforest
Amsterdam
Antarctic
Arctic
North Pole
Argentina
Asia
Athens
Atlantis
- Plato's Lost City
Australia
Austria
Aztecs
- Mexico
Baghdad
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Beachy
Head, England
Belgium
Benin
Berlin
Bermuda
Black
Rock Desert
Bohemia
Bolivia Bonneville
Utah History
Bonneville,
Utah, USA
Brazil
Brighton
- West Pier
British
Columbia
Buckingham
Palace
Bulgaria
Burkina
Faso
Burma
California
Canada
Canary
Islands
Cape
Horn
Cape
Verde
Cape
York - Au
Caribbean
Cayman
Islands
Central
Africa
Chichester
Harbour
Chile
China
Columbo
- Sri Lanka
Columbia
Corfu
Cowes,
Isle of Wight
Croatia
Crooked
Island, Bahamas
Cuba
Cyprus
Czechoslovakia
Darwin
- Australia
Daytona
Beach
Denmark
Eastbounre
Pier, England
Earthquakes
Ecuador
Egypt
Eindhoven Estonia
Equator
Europe
Falkland
Islands
Falmouth,
Cornwall
Fiji
Finland
France
Galapagos
Islands
Geography
Links
Geography
Mountains
Geography
Records
Geography
Resources
Geography
Statistics
|
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
- Links
Greece
Greenland
Guinea
Guinea
Bissau
Hawaii
Holland
the Nertherlands
Hollywood,
California, LA
Hong
Kong
Hungary
Hurricanes
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Links
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle
of Man
Isle
of Wight
- The
Needles
Israel
Italy
Ivory
Coast
Jakarta
- Java
Japan
Johannesburg
Jordan
Kent,
England
Kenya
Korea
Kuwait
Kyoto
Lanzarote,
Gran Canaria
Las
Vegas
Lebanon
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Life
on Earth
Lithuania
London
- Big
Ben
London
Eye
London
Houses
Parliament
London
- Buckingham
Palace
London
- Old
Bailey
London
- Overview
London
- The City
London
- Tower Bridge
London
- Trafalgar
Square
Luxembourg
Madame
Tussauds
Malaysia
Mali
Malta
Marshal
Islands
Mauritania
Maya
Empire -
Central America
Melbourne,
Australia
Middle
East
Melbourne,
Australia
Mexico
Monaco
Morocco
Mountains
Mumbai
Naples-
Italy
National
Geographic
Nepal
New
York
New
Zealand
Niger
Nigeria
North
Africa
Norway
Nova
Scotia
Oceans
and Seas
Oman
Pakistan
Palermo
- Sicily
Palestine
Palma
- Malorca
|
Panama
Canal - Links
Paris
Pendine
Sands
Peru
Philippines
Pisa,
Leaning Tower
Planet
Earth
Poland
Port
Moresby - PNG
Port
Said - Egypt
Portugal
Puerto
Rico
Qatar
Quebec
Rio
de Janeiro
Romania
Rome
Russia
Salt
Lake City
Samoa
Saudi
Arabia
Scandanavia
Scotland
Senegal
Siera
Leone
Singapore
Solomon
Islands
Somalia
South
Africa
South
America
Southampton
Spain
- Espana
Sri
Lanka - Links
Stonehenge
Sudan
Suez
Canal
Sundancer
Holiday Resort
Sussex,
England Index
Sweden
Switzerland
Sydney,
Australia
Syria
Tahiti
- Polynesia
- Links
Tahitian
- Men & Women Customs
Taiwan
Thailand
The
Gambia
Togo
Tokyo,
Japan
Tonga
- Polynesia
Toronto
Trinidad
- Lesser Antilles
Trinidad
and Tobago
Tsunami
Tunbridge
Wells, England
Tunisia
Turkey
Tuvalu
Islands
UAE
- United Arab Emirates
UK
Statistics
Ukraine
United
Kingdom
United
Kingdom -
Gov
USA
Uruguay
Vanuatu
Islands
Vatican
City
Venezuela
Venice
Vienna
Vietnam
Volcanoes
Volendam
Wales
Washington
D.C.
WAYN
Where Are You Now
Wealden
iron industry
Wendover
West
Africa
World
Peace Supporters
Yemen
Yugoslavia
Zurich
|
Kulo
Luna $billion dollar whale
When
a pirate whaler kills a small humpback whale, her giant friend sinks the
pirate ship to avenge the death, but is itself wounded. The pirates put a
price on the whale's head, but an adventurer in an advanced solar powered
boat races to beat the pirates and save the wounded animal.

A
heartwarming action adventure: Pirate whalers V Conservationists, with an
environmental message and a $Billion dollars riding on the winner.
Solar
Cola drinkers care about planet
earth
..
Thirst for Life

(330ml
Planet Earth can)

|
















